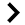YOUR EYES
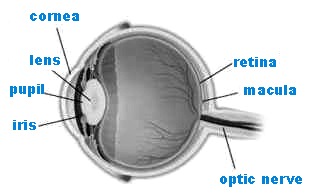
The EYE is an amazing organ. It is made up of various parts which determine what we see and how we see it. Light passes through the CORNEA, a transparent layer of the eye where 70 percent of light entering our eyes is focused or refracted.
Next, light rays pass through the LENS, which is responsible for about 30 percent of the focusing. The function of the lens s to adjust the focus of light onto the retina. The RETINA is where the image of what we see is projected.
Surrounding the cornea is the SCLERA, commonly known as “ the white of the eye “. It is the tough, opaque tissue that serves as the eye’s protective coat. Between the cornea and retina is the CHOROID or the middle layer of the eye. This layer contains numerous blood vessels, and supplies blood and nourishment to the tissues in the eye. The iris is a muscle that controls the size of the pupil and therefore, the amount of light that enters the eye. Also, the color of your eyes is determined by the iris. When nerve cells in the retina are stimulated by light, they send nerve impulses to the brain via the OPTIC NERVE. This allows us to perceive images.
ERROR OF REFRACTION
book an appointment
Emmetropia is the normal refractive condition of the eye, in which the rays of light are accurately focused on the retina.
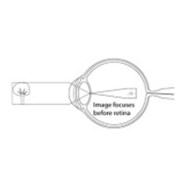
Myopia also known as nearsightedness is a condition of the eye in which parallel rays are focused in front of the retina, objects being seen distinctly only when near to the eye.
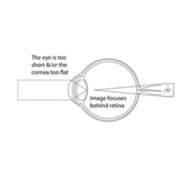
Hyperopia also known as farsightedness is a condition of the eye in which parallel rays of light are focused behind the retina, distant objects being seen more distinctly than near ones.
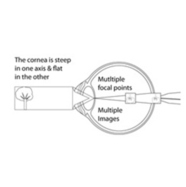
Astigmatism is a refractive error of the eye in which parallel rays of light from an external source do not converge on a single focal point on the retina which causes images near or far to appear blu